교차검증_그리드서치
01. 검증 세트
● 테스트세트를 사용해 모델의 성능을 개선해 나가다 보면 점점 테스트 세트에 적합한 모델이 됨
■ 테스트세트를 통해 일반화 성능을 올바르게 예측하기 힘들어짐
● 따라서 테스트세트를 사용하지 않고 훈련 세트를 또 다시 나눠 validation set을 이용
● 검증 세트 활용
1. 훈련 세트에서 모델을 훈련하고 검증 세트로 모델을 평가
2. 테스트하고 싶은 매개변수를 바꿔가며 가장 좋은 모델을 선택
3. 최적의 매개변수를 사용해 훈련 세트와 검증 세트를 합쳐 전체 훈련 데이터에서 모델을 다시 훈련
4. 테스트 세트에서 최종 점수를 평가
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import (train_test_split, cross_validate, StratifiedKFold,
GridSearchCV, RandomizedSearchCV)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from scipy.stats import uniform, randint
df = pd.read_csv("./data/wine.csv")
df.head()
x = df.drop("class", axis = 1)
y = df["class"]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.2, stratify = y, random_state = 26)
x_sub, x_val, y_sub, y_val = train_test_split(x_train, y_train, test_size = 0.2, stratify = y_train, random_state = 26)
print(x_sub.shape, x_val.shape, x_test.shape)
(4157, 3) (1040, 3) (1300, 3)
print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape)
(5197, 3) (1300, 3)
모델 훈련
dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 26)
dt.fit(x_sub, y_sub)
print(dt.score(x_sub, y_sub))
print(dt.score(x_val, y_val))
0.997834977146981
0.8567307692307692- 훈련 세트 점수가 지나치게 높고 검증 세트 점수와의 차이가 커서 과대적합 되었을 가능성이 높음
02. 교차 검증
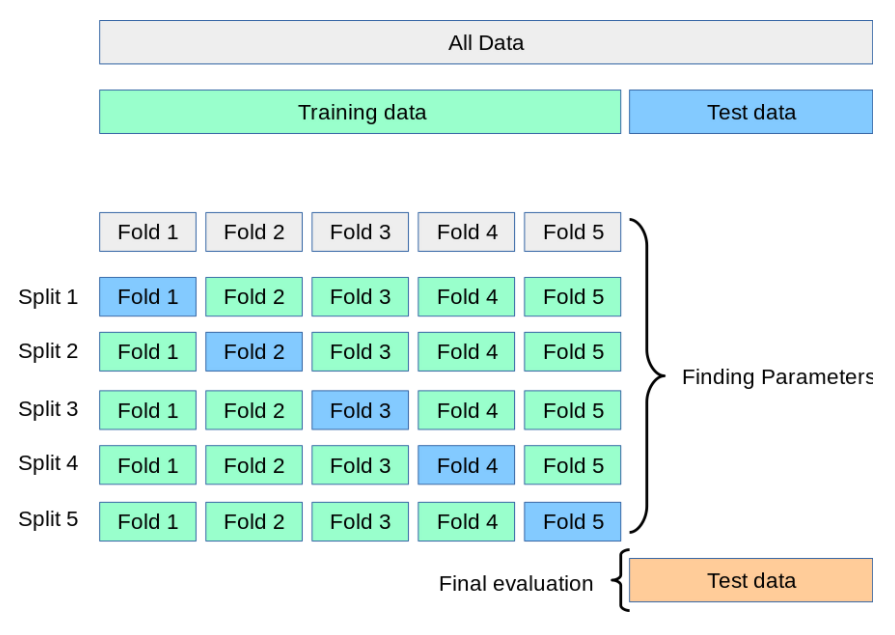
● 검증 세트를 만드는 과정에서 훈련 세트가 줄어들었음
■ 일반적으로 많은 데이터를 훈련에 사용할 수록 좋은 모델이 만들어질 가능성이 높음
○ 검증 세트를 줄이면 검증 점수가 불안정해져 올바른 모델 검증이 힘듦
○ 검증 세트를 늘리면 훈련 세트가 줄어듦
■ 따라서 cross validation(교차 검증)을 이용하여 안정적인 검증 점수를 얻으면서 훈련에 더 많은 데이터를 사용할 수 있음
# cross_validate 교차검증 함수
# cross_validate(모델 객체, 훈련 세트 전체 독립변수, 훈련 세트 전체 종속변수)
scores = cross_validate(dt, x_train, y_train)
print(scores)
{'fit_time': array([0.01556706, 0.00602984, 0.00803447, 0.00329709, 0.01141334]), 'score_time': array([0.00282884, 0.00197077, 0.00200438, 0. , 0.00161076]), 'test_score': array([0.86057692, 0.86346154, 0.84311838, 0.85851781, 0.86525505])}
● fit_time: 모델을 훈련하는 시간
● score_time: 모델을 검증하는 시간
● test_score: 검증 점수
■ 교차 검증의 최종 점수: test_score 점수의 평균
주의할점
● cross_validate는 훈련 세트를 섞지 않음
■ 지금의 예제에서는 train_test_split으로 전체 데이터를 섞었기 때문에 따로 섞을 필요는 없음
■ 교차 검증 시에 훈련 세트를 섞어야 한다면 splitter(분할기)를 지정해야 함
● 분할기
■ 교차 검증에서 폴드를 어떻게 나눌지 결정함
■ cross_validate 함수는 기본적으로 회귀모델일 경우 KFold를 사용하고, 분류 모델일 경우 종속 변수의 범주를 골고루 나누기 위해 StratifiedKFold를 사용함
# StratifiedKFold 10-폴드 교차 검증
splitter = StratifiedKFold(n_splits = 10, shuffle = True, random_state = 26)
scores = cross_validate(dt, x_train, y_train, cv = splitter)
scores
{'fit_time': array([0.01735663, 0.00700045, 0.00934124, 0.00463986, 0.00751066,
0.00699854, 0.00773859, 0.00599313, 0. , 0. ]),
'score_time': array([0.00203085, 0.00100064, 0.00201106, 0.00606918, 0.00099659,
0.00126529, 0.00100255, 0.00178266, 0. , 0.01565647]),
'test_score': array([0.86730769, 0.84615385, 0.87307692, 0.89230769, 0.85769231,
0.86346154, 0.85192308, 0.86127168, 0.83815029, 0.85356455])}
print(np.mean(scores["test_score"]))
0.8604909589447163
03. 그리드 서치
● 머신러닝 모델이 학습하는 파라미터: 모델 파라미터
● 모델이 학습할 수 없어서 사용자가 지정해야만 하는 파라미터: 하이퍼파라미터
● 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝 순서
1. 기본값으로 모델 훈련
2. 검증 세트의 점수나 교차 검증을 통해서 매개변수를 수정
■ 모델마다 적게는 1 ~ 2개, 많게는 5 ~ 6개 정도의 매개변수를 제공함
● 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝을 할 때에는 여러 매개변수의 최적값을 동시에 찾아야 함
■ 예) A매개변수의 최적값을 찾았다고 하더라도 B매개변수의 값이 바뀌면 A 매개변수의 최적값이 바뀜
■ 매개변수가 많아질수록 최적값을 찾는 과정이 더 복잡해짐
● 위의 문제를 해결하기 위해서 사이킷런의 GridSearh(그리드 서치)를 사용
■ 하이퍼 파라미터 탐색과 교차 검증을 한 번에 수행
params = {"min_impurity_decrease" : [0.0001, 0.0002, 0.0003, 0.0004, 0.0005]}
gs = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 26), params)
- 그리드 서치는 입력된 모델의 파라미터 값을 바꿔가면서 훈련을 실행함
- 현재 예제에서는 min_impurity_decrease 를 바꿔가면서 5회 훈련을 실행함
- GridSearchCV의 cv매개변수 기본값은 5이기 때문에 5-폴드 교차 검증을 수행함
- 따라서 1회 훈련마다 5회 교차 검증 * 5회 훈련 = 25회 모델을 훈련
gs.fit(x_train, y_train)

● 그리드서치는 훈련이 끝나면 검증 점수가 가장 높은 모델의 매개변수 조합으로 전체 훈련 세트에서 자동으로 다시 모델을 훈련함
■ 해당 모델은 best_estimator_ 속성에 저장됨
dt = gs.best_estimator_
print(dt.score(x_train, y_train))
print(dt.score(x_test, y_test))
0.931498941697133
0.8684615384615385
● 그리드 서치로 찾은 최적의 매개변수는 best_params 속성에 저장됨
gs.best_params_
{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0002}
● 각 매개변수에서 수행한 교차 검증의 평균 점수는 cv_result_ 속성의 "mean_test_score" 키에 저장됨
gs.cv_results_
{'mean_fit_time': array([0.00970445, 0.00635777, 0.00345225, 0.00649137, 0.00454855]),
'std_fit_time': array([0.0054189 , 0.00240595, 0.00690451, 0.00499204, 0.00578272]),
'mean_score_time': array([0.00226812, 0.00125732, 0.00018325, 0.00099993, 0.00020075]),
'std_score_time': array([1.88287786e-03, 6.61200853e-04, 3.66497040e-04, 7.97901179e-07,
4.01496887e-04]),
'param_min_impurity_decrease': masked_array(data=[0.0001, 0.0002, 0.0003, 0.0004, 0.0005],
mask=[False, False, False, False, False],
fill_value=1e+20),
'params': [{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0001},
{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0002},
{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0003},
{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0004},
{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0005}],
'split0_test_score': array([0.87211538, 0.87596154, 0.86923077, 0.87115385, 0.85865385]),
'split1_test_score': array([0.86442308, 0.87115385, 0.86442308, 0.86538462, 0.87115385]),
'split2_test_score': array([0.86236766, 0.86525505, 0.8614052 , 0.86044273, 0.85755534]),
'split3_test_score': array([0.87006737, 0.86717998, 0.87391723, 0.87006737, 0.87487969]),
'split4_test_score': array([0.87680462, 0.87487969, 0.87969201, 0.86717998, 0.86910491]),
'mean_test_score': array([0.86915562, 0.87088602, 0.86973366, 0.86684571, 0.86626953]),
'std_test_score': array([0.00522632, 0.00417671, 0.00654965, 0.00379957, 0.00692772]),
'rank_test_score': array([3, 1, 2, 4, 5])}
gs.cv_results_["mean_test_score"]
array([0.86915562, 0.87088602, 0.86973366, 0.86684571, 0.86626953])
best_idx = np.argmax(gs.cv_results_["mean_test_score"])
best_idx
1
gs.cv_results_["params"][best_idx]
{'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0002}
min_impurity_decrease, max_depth, min_sample_split 의 최적값 찾기
- min_impurity_decrease: 노드를 분할하기 위한 불순도 감소 최소량
- max_depth: 트리의 깊이 제한
- min_samples_split: 노드를 나누기 위한 최소 샘플 수
params = {"min_impurity_decrease" : np.arange(0.0001, 0.001, 0.0001), # 총 9개
"max_depth" : range(5, 20), # 총 15개
"min_samples_split": range(2, 100, 10)} # 총 10개
- 위 파라미터로 수행할 교차 검증 횟수는 9 * 15 * 10 = 1350회
- 기본 5-폴드 교차 검증을 하기 때문에 1350 * 5 = 6750번의 훈련을 수행
gs = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 26), params, n_jobs = -1)
# n_jobs = -1 병렬수행(동시수행):CPU가 허용하는 한 최대의 job, 함부로 쓰면 서버가 터질 수 있음
gs.fit(x_train, y_train)
C:\ProgramData\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\numpy\ma\core.py:2820: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in cast
_data = np.array(data, dtype=dtype, copy=copy,

# 최상의 매개변수 조합
gs.best_params_
{'max_depth': 15, 'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0002, 'min_samples_split': 2}
# 최상의 교차 검증 점수
np.max(gs.cv_results_["mean_test_score"])
0.8720404234841194
04. 랜덤 서치
- 매개변수의 값이 수치일 때 값의 범위나 간격을 정하기 어려울 수 있고 너무 많은 매개변수 조건이 있어서 그리드 서치 수행시간이 오래 걸릴 수 있음
- RandomSearch(랜덤 서치)는 매개변수 값의 목록을 전달하는 것이 아니라 매개변수를 샘플링 할 수 있는 확률 분포 객체를 전달함
- 균등 분포에서 샘플링
- 주어진 범위에서 고르게 값을 생성
- randint: 정수
- uniform: 실수
randint(0, 10).rvs(10)
array([7, 3, 2, 2, 5, 0, 2, 0, 6, 9], dtype=int64)
uniform(0, 1).rvs(10)
array([0.10347328, 0.32930277, 0.69281648, 0.83264939, 0.1241029 ,
0.33770456, 0.97565234, 0.50735057, 0.58292495, 0.77200362])
params = {"min_impurity_decrease" : uniform(0.0001, 0.001),
"max_depth" : randint(5, 50),
"min_samples_split": randint(2, 100),
"min_samples_leaf": randint(2, 100)}
rs = RandomizedSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state = 26), params, n_iter = 100,
n_jobs = -1, random_state = 26)
rs.fit(x_train, y_train)
- 위 params에 정의된 매개변수 범위에서 총 100번 샘플링하여 교차 검증을 수행
- 그리드서치보다 교차 검증 수를 줄이면서도 넓은 영역을 효과적으로 탐색
print(rs.best_params_)
{'max_depth': 7, 'min_impurity_decrease': 0.00038272396340744997, 'min_samples_leaf': 2, 'min_samples_split': 53}
np.max(rs.cv_results_["mean_test_score"])
0.8693455245428297
print(gs.best_estimator_.score(x_test, y_test))
print(rs.best_estimator_.score(x_test, y_test))
0.8676923076923077
0.8569230769230769'08_ML(Machine_Learning)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 22_랜덤포레스트_문제(상한 개사료) (0) | 2025.04.11 |
|---|---|
| 21_트리 앙상블 (0) | 2025.04.10 |
| 19_의사 결정 나무 (2) | 2025.04.09 |
| 18_확률적 경사 하강법 (0) | 2025.04.09 |
| 16_로지스틱 회귀분석_심화 (1) | 2025.04.08 |